What is Diabetic Retinopathy?
Living with diabetic retinopathy can be challenging, but understanding the condition helps. Diabetic retinopathy is an eye disease caused by high blood sugar. Over time, diabetes can damage the tiny blood vessels in your retina. The retina is the part of your eye that senses light. When these vessels are harmed, vision problems can develop. According to the CDC, diabetic retinopathy is a leading cause of vision loss in adults. Early care and regular checkups are important for protecting vision with diabetes.
Common Symptoms
At first, you may not notice any symptoms. However, as the disease progresses, signs can appear. It is important to watch for changes in your vision. Early detection helps with managing diabetic retinopathy.
If you notice any of these symptoms, contact your eye doctor right away. Quick action can help prevent further vision loss.
Causes and Risk Factors
Diabetic retinopathy develops when high blood sugar damages blood vessels in the retina. Over time, these vessels can leak or become blocked. Several factors increase your risk:
Therefore, managing your diabetes and overall health is key to lowering your risk.
Diagnosis and Monitoring
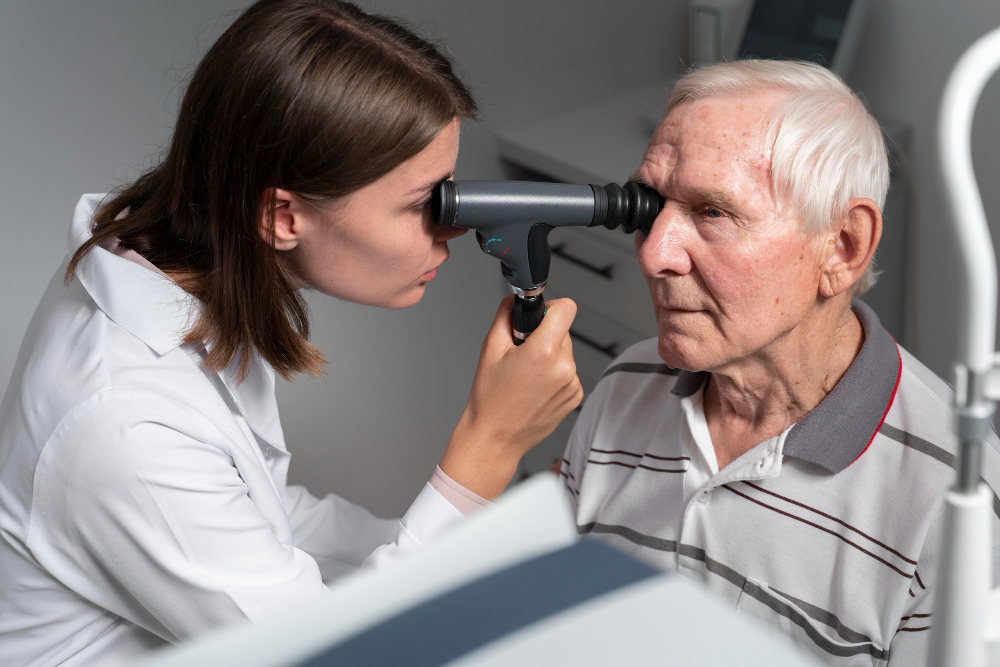
Regular eye exams are vital for diabetic eye disease care. Your eye doctor will use special tools to check your retina. Often, they will dilate your pupils to get a better view. Early diagnosis allows for better treatment options. The American Diabetes Association recommends yearly eye exams for people with diabetes. In some cases, your doctor may suggest more frequent visits.
Treatment Options
Treatment depends on how severe your diabetic retinopathy is. Early stages may only need careful monitoring and better blood sugar control. However, advanced cases may require medical procedures. Common treatments include:
Because each case is different, your eye specialist will recommend the best plan for you.
Daily Life: Tips for Managing Diabetic Retinopathy
Living with diabetic retinopathy means making healthy choices every day. Simple steps can help protect your vision and improve your quality of life. Here are some practical tips:
Additionally, keep a list of questions for your doctor. This helps you stay informed about your eye health.
Prevention and Eye Health Maintenance
Although diabetic retinopathy cannot always be prevented, you can lower your risk. Good diabetes management is the best way to protect your eyes. Try these eye health tips for diabetics:
With these steps, you can help prevent serious vision problems.
When to See an Eye Specialist
It is important to see an eye specialist if you have diabetes. Even if you do not notice changes, regular visits are key. However, seek help right away if you:
Early treatment can save your sight. Access to care may vary by location, so ask your doctor about local resources.
In summary, living with diabetic retinopathy requires daily care and regular check-ups. Consult Dr. Sudha for personalized advice on managing diabetic retinopathy.